8 min read
An Overview: the TON Ecosystem
Hidden Gem of High-Speed Blockchain Innovation

Introduction
According to CoinMarketCap, TON is among the top five most visited and read about blockchain at the time of writing. The project’s currency market capitalization has also risen in recent days, and yet many crypto enthusiasts are oblivious to this project. The Luganodes research team has come to their aid! Continue reading to learn more about the network.
# What is it?#CMCCommunity Ranking 🏆
— CoinMarketCap (@CoinMarketCap) November 9, 2022
There are a lot of #crypto updates to catch up on this past week! Especially news from @SuperLitho @Puli_Token @RunOnFlux @PositionEx @ton_blockchain 🔥#CoinMarketCap #CMC #crypto #cryptonews pic.twitter.com/6K4LSNJoa8
The Open Network (TON) is a fast, secure, and scalable blockchain and network project capable of handling millions of transactions per second if necessary, and it is both user-friendly and service provider-friendly, according to the white paper published by TON in 2021. The ultimate purpose of the network is to host all feasible apps and dapps currently suggested and envisioned. TON is equivalent to a massively distributed supercomputer, or more accurately, a massive super server designed to host and deliver a range of services.
The blockchain project was proposed by the developers of the Telegram instant messaging service. The TON community, on the other hand, is currently developing and steering the blockchain. The project touts itself as a Layer 1 and Layer 2 project developed from the bottom up to become a decentralized message hosting and storage solution. The Shard chain is in charge of smart contracts, whereas the Master chain is in charge of consensus. The chain supports smart contracts, tokenization of social networks and messaging applications, cross-chain bridges, and internet protocols such as TON DNS.
Unlike Bitcoin and Ethereum, which are currently relegated to being a store of wealth and are too slow to be utilized as a medium of trade, TON’s design is based on the ideals of every day and hassle-free usage. Its low fuel costs, rapid throughput, user-friendly applications, ecologically beneficial nature, and wide array of features ensure this. Through sharding, the network is capable of processing millions of transactions.
The community is granted the ability to alter information in an existing block, which may be used to nullify unlawful transactions, and use as defence against a “51% attack”. Bridges can be used connect to external networks, and bridges to Ethereum and Binance Smart Chain are already operational. Developers may use smart contracts to launch their own projects in the TON ecosystem.
Features:
TON intends to offer an ecosystem comprised of many of the capabilities listed below in its meticulously planned roadmap. Many of these services have already been released and have garnered a positive response.
TON Services: It is a global platform for third-party services, provides decentralized web browsing, and has user-friendly interfaces. That is, independent developers can produce network-based apps.
TON Payments: is a micropayments platform. Bots, humans, and services can utilize it for lightning-fast off-chain transactions.
TON Proxy: An anonymizer for TON nodes, similar to an anonymous I2P network. The proxy allows you to build blockchain-based decentralized VPNs and exempts dApps from censorship.
TON DNS: The “Domain Name System”, conceptually similar to the mechanism used in web2, assigning readable names to accounts, services, nodes, and smart contracts amounts to better UX.
TON Storage: A distributed data storage decentralized counterpart of file hosting. It is based on smart contract technology. The storage is appropriate for working with big volumes of data.
Architecture:
The TON network is composed of three layers. The master chain makes up the first level, which employs the Proof-of-Stake algorithm to achieve consensus. The master chain is the primary chain of the TON network, and all operations in TON are executed on the master chain. The master chain stores the hashes of the work and shard chains. The second layer is made up of work chains that are linked to the master chain and may scale up to 2³² in number. These chains rely on their own consensus processes, as well as VM-enabled smart contracts. All of these chains can communicate with one another via the master chain, similar to how Polkadot achieves interoperability. The third level is made up of shard chains. Each work chain can have a maximum of 2⁶⁰ shards. These shards render work chains with nearly unlimited scalability.
To become a TON network validator, one must have access to high-performance hardware on a highly accessible network, as well as a large amount of $TON as a stake (an average of 600,000 $TON at the time of writing). The average daily income earned by a validator node through incentives with the average stake is around 270 $TON per day (as of May 2022). Although becoming a validator on the network is not an easy undertaking, the number of validators on TON has steadily increased in the previous year, increasing the extent of decentralization on the network.

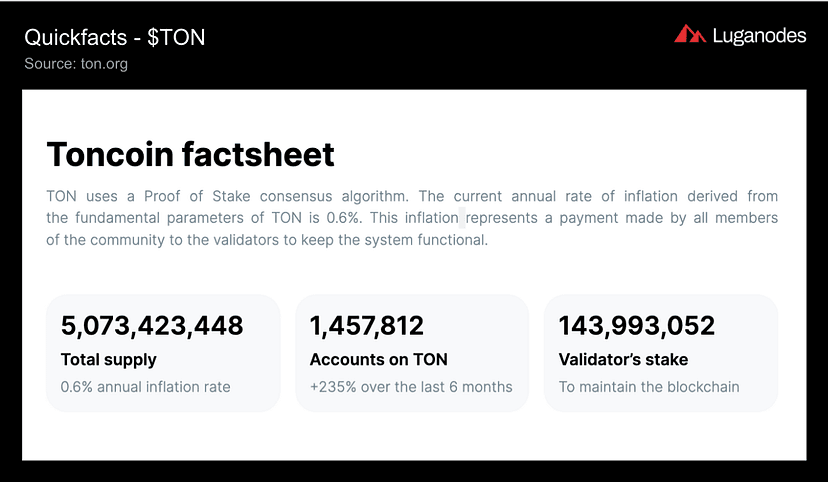
Tokenomics:
The TON project’s native coin is called $TON (formerly $GRAM). This digital token, like many blockchain networks, may be used to
- Pay for transactions with gas and engage with smart contracts.
- Perform native cross-chain network activities. Since $TON is the master chain token, and each work chain circulates its own token that is interoperable with $TON, these actions are feasible.
- The token is also used to pay for network resource access. Accessing the decentralized storage system (TON Storage), the DNS service (TON DNS), or the services implemented in the TON Services layer, for example.
- New staking nodes are deployed for the master chain, as well as for work chains and shard chains.
- Having $TON allows a user to participate in on-chain governance procedures.
The mining protocol of the chain is majorly centered around achieving the goals of maximum utilization of CPUs and GPUs. The entire quantity of $TON is limited to 5 GigaTON (i.e., 5B $TON coins or 5 x 1⁰¹⁸ Nanos). The network intends to distribute this money in a constant stream by rewarding validators for mining new blocks on the master chain and shard chain. These rewards are projected to be 20% of the validator’s yearly stake, assuming the validator dutifully executes its tasks and signs all blocks with no downtime or malicious activity. This will result in a 2% annual inflation rate. To combat inflationary pressure, a portion of the validator’s stake will be reduced, and a bigger percentage will be burnt, reducing the overall quantity of the token. This deflation will guarantee that the supply of $TON does not exceed the predicted quantity.
 The potential of $TON is demonstrated in its solid position even after the FTX fiasco. The coin’s charts remain bright green, with a 12% rise in the week after the FTX crash. This token boasts a market capitalization of about $2.1B and ranks among the top 30 cryptocurrencies in the world.
The potential of $TON is demonstrated in its solid position even after the FTX fiasco. The coin’s charts remain bright green, with a 12% rise in the week after the FTX crash. This token boasts a market capitalization of about $2.1B and ranks among the top 30 cryptocurrencies in the world.
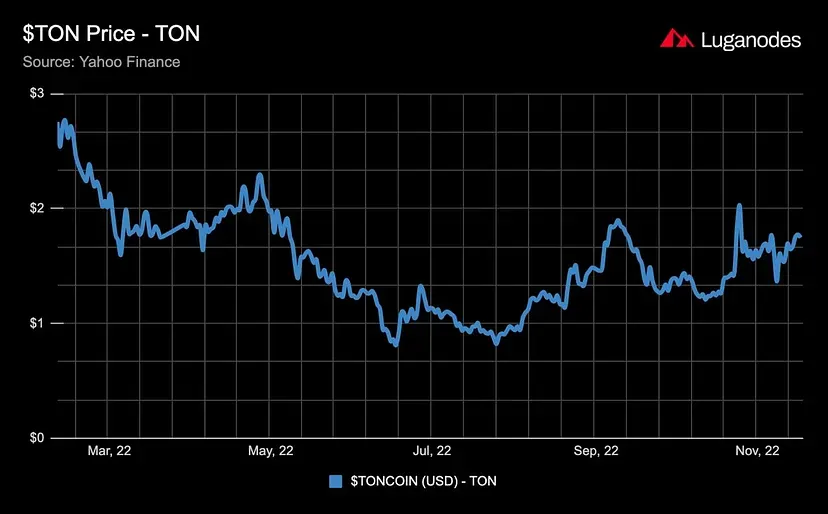 This upward trajectory can likely be attributed to the network’s recent username auction, which was a huge success. This auction is a step toward allowing social media users to publicly verify ownership of their handles by tokenizing them on the TON blockchain. The trade volume associated with this phenomenon has been enormous; for example, the handle “@dogecoin” was sold for a stunning 350,000 $TON ($546,000)!
This upward trajectory can likely be attributed to the network’s recent username auction, which was a huge success. This auction is a step toward allowing social media users to publicly verify ownership of their handles by tokenizing them on the TON blockchain. The trade volume associated with this phenomenon has been enormous; for example, the handle “@dogecoin” was sold for a stunning 350,000 $TON ($546,000)!
#CMCCommunity Ranking 🏆
— CoinMarketCap (@CoinMarketCap) November 9, 2022
There are a lot of #crypto updates to catch up on this past week! Especially news from @SuperLitho @Puli_Token @RunOnFlux @PositionEx @ton_blockchain 🔥#CoinMarketCap #CMC #crypto #cryptonews pic.twitter.com/6K4LSNJoa8
The initiative has also received the backing of DWF Labs, a well-known market maker. Their backing for the TON effort culminated in a $10 million investment in the project. This effort from DWF Labs will most certainly increase TON’s volume across compatible platforms.
DWF Labs will invest $10M in the $TON ecosystem@DwfLabs has pledged an investment to spur development in the growing TON ecosystem and will assist in creating tokens, market-making, and listing #Toncoin on exchanges. pic.twitter.com/QBt969Vyov
— TON 💎 (@ton_blockchain) November 18, 2022
Conclusion:
The TON network finest exemplifies the phrase “pick yourself up, dust yourself off, and get back in the saddle”. The network has implemented several elements in order to achieve an ambitious aim of providing speeds of up to a million transactions per second.

The unique design, which comprises not just one chain, but master chains, work chains, shard chains, and hundreds of shards, will enable security, scalability and speed. With the release of dapps and conventional centralised programmes like CryptoBot, Bridge TON-ETH, Bridge TON-BSC, and Mining Bot, it appears TON is just getting started
About Luganodes
Luganodes is a world-class, Swiss-operated, non-custodial blockchain infrastructure provider that has rapidly gained recognition in the industry for offering institutional-grade services. It was born out of the Lugano Plan B Program, an initiative driven by Tether and the City of Lugano. Luganodes maintains an exceptional 99.9% uptime with round-the-clock monitoring by SRE experts. With support for 45+ PoS networks, it ranks among the top validators on Polygon, Polkadot, Sui, and Tron. Luganodes prioritizes security and compliance, holding the distinction of being one of the first staking providers to adhere to all SOC 2 Type II, GDPR, and ISO 27001 standards as well as offering Chainproof insurance to institutional clients.